Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kondo, Satoru; Tobita, Yoshiharu
JAEA-Research 2019-009, 382 Pages, 2020/03
The SIMMER-III computer code, developed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA, the former Power Reactor and Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation), is a two-dimensional, multi-velocity-field, multi-component fluid-dynamics code, coupled with a space- and time-dependent neutron kinetics model. The code is being used widely for simulating complex phenomena during core-disruptive accidents (CDAs) in liquid-metal fast reactors (LMFRs). In parallel to the code development, a comprehensive assessment program was performed in two phases: Phase 1 for verifying individual fluid-dynamics models; and Phase 2 for validating its applicability to integral phenomena important to evaluating LMFR CDAs. The SIMMERIII assessment program was participated by European research and development organizations, and the achievement of Phase 1 was compiled and synthesized in 1996. This report has been edited by revising and reproducing the original 1996 informal report, which compiled the achievement of Phase 1 assessment. A total of 34 test problems were studied in the areas: fluid convection, interfacial area and momentum exchange, heat transfer, melting and freezing, and vaporization and condensation. The problems identified have been reflected to the Phase 2 assessment and later model development and improvement. Although the revisions were made in the light of knowledge base obtained later, the original individual contributions by the participants, both positive and negative, are retained except for editorial changes.
Wakai, Takashi; Machida, Hideo*; Arakawa, Manabu*; Yanagihara, Seiji*; Suzuki, Ryosuke*; Matsubara, Masaaki*
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
This paper studies crack opening displacement (COD) evaluation methods used in Leak-Before-Break (LBB) assessment of Sodium cooled Fast Reactor (SFR) pipe. For SFR pipe, the continuous leak monitoring will be adopted as an alternative to a volumetric test of the weld joints under conditions that satisfy LBB. The sodium pipes are made of ASME Gr.91 (modified 9Cr-1Mo steel). Thickness of the pipes is small, because the internal pressure is very small. Modified 9Cr-1Mo steel has a relatively large yield stress and small work hardening coefficient comparing to the austenitic stainless steels which are currently used in the conventional plants. In order to assess the LBB behavior of the sodium pipes made of modified 9Cr-1Mo steel, the coolant leak rate from a through wall crack must be estimated properly. Since the leak rate is strongly related to the crack opening displacement (COD), an appropriate COD assessment method must be established to perform LBB assessment. However, COD assessment method applicable for SFR pipes - having thin wall thickness and made of small work hardening material - has not been proposed yet. Thus, a COD assessment method applicable to such a pipe was proposed in this study. In this method, COD was calculated by classifying the components of COD; elastic, local plastic and fully plastic. In addition, the verification of this method was performed by comparing with the results of a series of four-point bending tests using modified 9Cr-1Mo steel pipe having a circumferential through wall notch. As a result, in some cases, COD were over-estimated especially for large cracks. Although the elastic component of COD is still over-estimated for large cracks, leak evaluation from small cracks is much more important in LBB assessment. Therefore, this study recommends that only the elastic component of COD should be adopted in LBB assessment of SFR pipes.
Wakai, Takashi; Machida, Hideo*; Arakawa, Manabu*; Kikuchi, Koichi*
Proceedings of ASME Symposium on Elevated Temperature Applications of Materials for Fossil, Nuclear, and Petrochemical Industries, 7 Pages, 2018/04
A simplified J-integral evaluation method applicable to unstable failure analysis in Leak Before Break (LBB) assessment of Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (SFR) in Japan was proposed. Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel is supposed to be a candidate material for the coolant systems of SFR in Japan. This steel has relatively high yield strength and poor fracture toughness comparing to those of conventional austenitic stainless steels. In addition, SFR pipe has small thickness and large diameter. As a J-integral evaluation method for circumferential through-wall crack in a cylinder, EPRI has proposed a fully plastic solution method. However, the geometry of SFR pipe and material characteristics of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel exceed the applicable range of EPRI's method. Therefore, a series of elastic, elasto-plastic and plastic finite element analyses (FEA) were performed for a pipe with a circumferential through-wall crack to propose a J-integral evaluation method applicable to such loading conditions. J-integrals obtained from the FEA were resolved into elastic, local plastic and fully plastic components. Each component was expressed as a function of analytical parameter, such as pipe geometries, crack size, material characteristics and so on. As a result, a simplified J-integral evaluation method was proposed. The method enables to conduct 2 parameter failure analysis using J-integral without any fracture mechanics knowledge.
Kitano, Akihiro; Takegoshi, Atsushi*; Hazama, Taira
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(7), p.992 - 1008, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:60.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)A feedback reactivity measurement technique was developed based on a reactivity model featuring components that depend on the reactivity coefficients, denoted as reactor power (K ) and reactor vessel inlet temperature (K
) and reactor vessel inlet temperature (K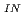 ). This technique was applied to the feedback reactivity experiment conducted in the Monju system start-up test in May 2010. A thorough evaluation considering all possible biases and uncertainties revealed that the reactivity coefficients can be evaluated with a measurement uncertainty smaller than 3%. The evaluated reactivity coefficients were simulated considering the temperature distribution in the core. The C/E value of K
). This technique was applied to the feedback reactivity experiment conducted in the Monju system start-up test in May 2010. A thorough evaluation considering all possible biases and uncertainties revealed that the reactivity coefficients can be evaluated with a measurement uncertainty smaller than 3%. The evaluated reactivity coefficients were simulated considering the temperature distribution in the core. The C/E value of K showed good agreement between calculated and measured values within the established uncertainty, and the value of K
showed good agreement between calculated and measured values within the established uncertainty, and the value of K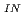 was consistent with that reported in a previous isothermal temperature coefficient experiment. The measured and calculated fuel subassembly outlet temperatures also agreed well within 0.2
was consistent with that reported in a previous isothermal temperature coefficient experiment. The measured and calculated fuel subassembly outlet temperatures also agreed well within 0.2 C.
C.
Hiroi, Hiroshi*; Arai, Masanobu; Kisohara, Naoyuki
Dai-21-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 3 Pages, 2016/06
The purpose of fast breeder reactors (FBR) and the role of Monju were discussed in Ministry of education, culture, sports science and technology-Japan (MEXT) after the Fukushima NNP accident. The discussion has concluded that FBRs contribute to energy security and reduction of high-level radioactive waste, and that Monju is to be utilized to demonstrate these usefulness and to implement international contributions. This paper addresses anticipated R&D results from Monju on the basis of the enforcement of new nuclear regulation, the energy situations in Japan and the international status of FBR development and collaborations.
Sector of Fast Reactor Research and Development
JAEA-Evaluation 2015-005, 77 Pages, 2015/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) asked the advisory committee "Evaluation Committee of Research and Development Activities for Fast Reactor Cycle" (the Committee) to assess "R&D Programs on FBR/FR Cycle Technologies" and "R&D Programs on Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor Monju and its Related Activities" during the period between FY2010 and FY2014, in accordance with "General Guideline for the Evaluation of Government R&D Activities" by Japanese Cabinet Office, "Guideline Evaluation of R&D in Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology" and "Regulation on Conduct for Evaluation R&D Activities" by JAEA. This report summarizes results of proposal by the Committee.
Tone, Tatsuzo
JAERI-Review 2001-002, 568 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
; Ohno, Shuji;
JNC TN2400 2000-006, 56 Pages, 2000/12
Sodium combustion analyses were performed using ASSCOPS version 2.1 in order to obtain background data for evaluating the validity of the mitigation system against secondary sodium leak of MONJU. The calculated results are summarized as follows. (1)Peak atmospheric pressure  4.3 kPa[gage] (2)Peak floor liner temperature
4.3 kPa[gage] (2)Peak floor liner temperature  870
870 C, Maximum thinning of liner
C, Maximum thinning of liner  2.6mm (3)Peak hydrogen concentration <2% (4)Peak floor liner temperature in the spilt sodium storage eell
2.6mm (3)Peak hydrogen concentration <2% (4)Peak floor liner temperature in the spilt sodium storage eell  400
400 C , Peak floor concrete temperature in the spilt sodium storage cell
C , Peak floor concrete temperature in the spilt sodium storage cell  140
140 C.
C.
; ; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; ; ; ;
JNC TN2400 2000-005, 103 Pages, 2000/12
Inelastic analyses of the floor liner subjected to thermal loading due to sodium leakage and combustion were carried out, considering thinning of the liner plate due to molten salt type corrosion. Because the inelastic strain obtained by the analyses stayed below the ductility limit of the material, mechanical integrity, i.e., there exist no through-wall crack on the floor liner, was confirmed. Partial structural model tests were conducted, with a band of local thinning of the liner plate. Displacements were controlled to give specimens much larger strains than those obtained by the inelastic analyses above. No through-wall crack was observed by these tests. Mechanical integrity of the floor liner was confirmed by these results of the inelastic analyses and the partial structural model tests.
; Inagaki, Tatsutoshi*
JNC TY1400 2000-003, 92 Pages, 2000/08
Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) and Japan Atomic Power company (JAPCO, that is the representative of the electric utilities in Japan) have established a new organization to develop a commercialized fast breeder reactor (FBR) cycle system since July 1, 1999 and feasibility studies (F/S) have been undertaken in order to determine the promising concepts and to define the necessary R&D tasks. In the first two-year phase, a number of candidate concepts will be selected from various options, featuring innovative technologies. In the F/S, the options are evaluated and conceptual designs are examined considering the attainable perspectives for following: (1) ensuring safety, (2) economic competitiveness to future LWRs, (3) efficient utilization of resources, (4) reduction of environmental burden and (5) enhancement of nuclear non-proliferation. The F/S should also guide the necessary R&D to commercialize FBR cycle system.
; ; ; ;
JNC TN9400 2000-066, 52 Pages, 2000/06
Phase I of feasibility studies on commercialized fast reactor system is being peformed for two years from Japanese Fiscal Year 1999. In this report, results of the study on fluid fuel reactors (especialiy a molten salt fast breeder reactor concept) are described from the viewpoint of technical and economical concerns of the plant system design. ln JFY1999, we have started to investigate the fluid fuel reactors as alternative concepts of sodium cooled FBR systems with MOX fuel, and selected the unique concept of a molten chloride fast, breeder reactor, whose U-Pu fuel cycle can be related to both light water reactors and fast breeder reactors on the basis of present technical data and design experiences. We selected a preliminary composition of molten fuel and conceptual plant design through evaluation of technical and economical issues essential for the molten salt reactors and then compared them with reference design concepts of sodium cooled FBR systems under limited information on the molten chloride fast breeder reactors. The following results were obtained. (1)The molten chloride fast breeder reactors have inherent safety features in the core and plant performances, ad the fluid fuel is quite promising for cost reduction of the fuel fabrication and reprocessing. (2)On the other hand, the inventory of the molten chloride fuel becomes high and thermal conductivity of the coolant is inferior compared to those of sodium cooled FBR systems, then, the size of main components such as lHX's becomes larger and the amount of construction materials is seems to be increased. (3)Furthermore economical vessel and piping materials which contact with the molten chloride salts are required to be developed. From the results, it is concluded that further steps to investigate the molten chloride fast breeder reactor concepts are too early to be conducted.
Takata, Takashi; Yamaguchi, Akira
JNC TN9400 2000-065, 152 Pages, 2000/06
ln the liquid metal fast reactor (LMFR) using liquid sodium as a coolant, it is important to evaluate the effect of the sodium combustion on the structure, etc. Most of the previous analytical works are based on a zone model, in which the principal variables are treated as volume-average quantities. Therefore spatial distribution of gas and structure temperatures, chemical species concentration are neglected. Therefore, a multi-dimensional sodium combustion analysis code AQUA-SF (Advanced simulation using Quadratic Upstream differencing Algorithm - Sodium Fire version) has been developed for the purpose of analyzing the sodium combustion phenomenon considering the multi-dimensional effect. This code is based on a multi-dimensional thermal hydraulics code AQUA that employs SIMPLEST-ANL method. Sodium combustion models are coupled with AQUA; one is a liquid droplet model for spray combustion, and the other is a flame sheet model for pool combustion. A gas radiation model is added for radiation heat transfer. Some other models necessary for the sodium combustion analysis, such as a chemical species transfer, a compressibility, are also added. ln AQUA-SF code, bounded QUICK method in space scheme and bounded three-point implicit method in time scheme are implemented. Verification analyses of sodium combustion tests shown in the following have been carried out. (1)pool combustion test (RUN-D1) (2)spray combustion test (RUN-E1) (3)sodium leakage combustion test (Sodium Fire Test-II) (4)smaII-scale leakage combustion test (RUN,F7-1) ln each verification analysis, good agreements are obtained and the validity of AQUA-SF code is confirmed.
JNC TN4400 2000-002, 33 Pages, 2000/06
An on-site plant analyzer can provide analysis support in evaluating plant dynamic characteristics when unplanned events occur in a nuclear power station. The plant analyzer contains a plant-dynamics analysis code, which efficiently and quickly analyzes the plant dynamic characteristics. Elements being developed for the on-site plant analyzer include utilities to build plant models for performing analyses and to retrieve plant operation data. The addition of these elements to the analysis code supports the plant-dynamics analysis works in MONJU, in particular, to assist the analyses of start up tests. The system contains the FBR plant-dynamics analysis code "Super-COPD", which is based on the "COPD" code that was used in the safety licensing of MONJU. One feature of the system is that all operations, e.g., assembling plant models for analysis, are prepared using a GUI (Graphical user Interface). In addition to this feature, the system is able to retrieve directly on- and off-line plant data from MIDAS, the Monju Integrated Data Acquisition System. These plant data are used to supply time-dependent boundary conditions for the plant analysis models. For this report, two case studies were performed. First, the analysis result of a turbine trip test at 40% power operation using the full plant model is described. For the second, performance of the IHX model was evaluated using retrieved plant data for boundary conditions. With the development of this system, improvement in the efficiency of analyses of MONJU start-up tests is expected.
Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Nakatsuka, Toru; Iwamura, Takamichi
JAERI-Conf 2000-010, 267 Pages, 2000/06
no abstracts in English